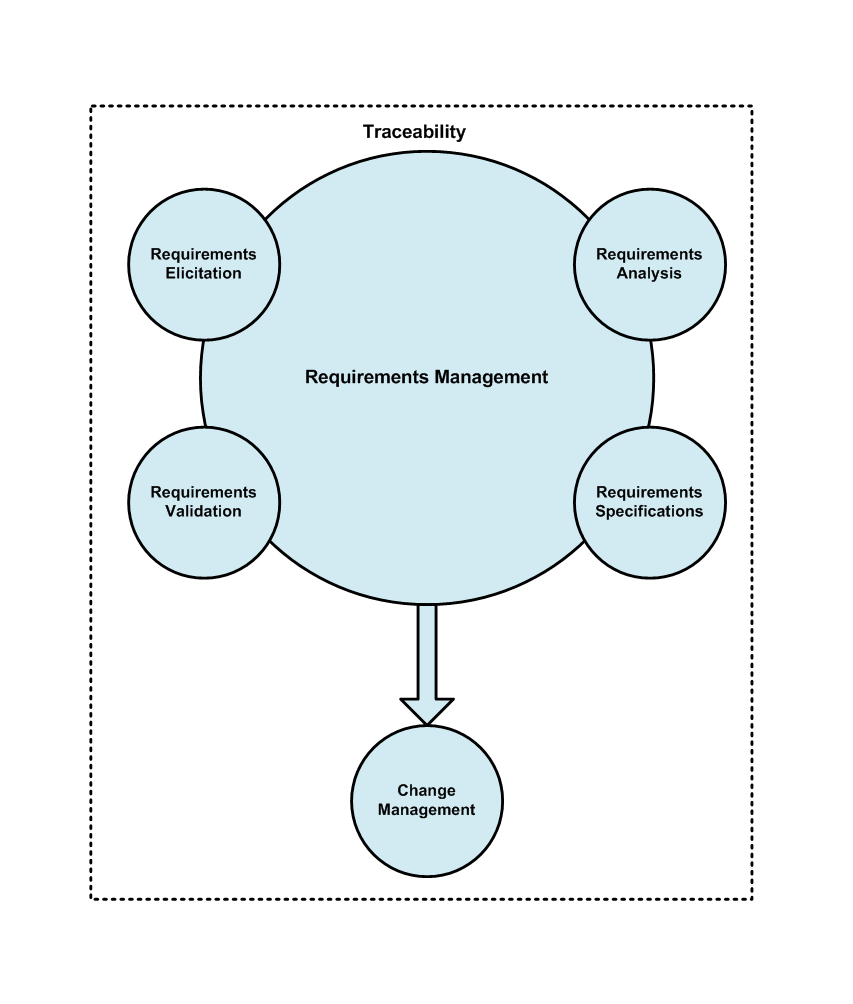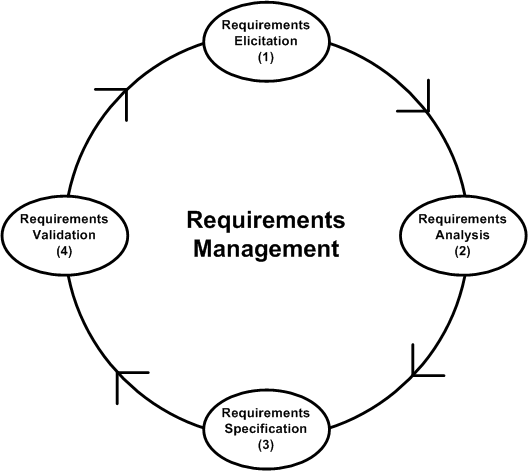
Requirements Management
Requirements Management is the process of documenting, analyzing, tracing, prioritizing and agreeing on requirements and then controlling change and communicating to relevant stakeholders. It is a continuous process throughout a project. The Requirements Management tools available in the marketplace are many and they are as good as their users knowledge of using them. they include:
-
MS Excel Spreadsheets;
-
Requisitepro (by IBM);
-
Dynamic Object Oriented Requirements System (DOORS) by HP;
-
Quality Centre (QC) by HP;
-
CalibreRM by Borland;
-
JIRA by Attlassian; and more.
Requirements Types
The typical deliverables of the BA, include:
-
Business Case (BC) a document that outlines business justification, shareholders’ risk (financial and technological) and Return On Investment (ROI).
-
Business Requirements, i.e. business plan, KPI, project plan.
-
Functional Requirements (FR), i.e. data models, technical specifications, use case scenarios, work instructions, reports. The plan for implementing functional requirements is detailed in the system design.
-
Non-functional Requirements (NFR), i.e. criteria that can be used to judge the operation of a system, rather than specific behaviors. This should be contrasted with functional requirements that define specific behavior or functions. The plan for implementing non-functional requirements is detailed in the system architecture.
-
Legal & Legislative Requirements (L&LR) i.e. reflection of the exterier environment that the organisation must comply with.
-
"As-Is" Processes Mapping i.e. flowcharts that describe the behaviour of the current system(s).
-
"To-Be" Processes Mapping i.e. flowcharts that describe the behaviour of the future system(s).